The ball mill is a widely used piece of equipment in various industries for grinding materials into fine powders. It operates on the principle of impact and attrition, where the grinding media (typically steel balls) collide with the material being ground. This mechanism ensures that the material is broken down into smaller particles, making it suitable for many processes, such as in the production of cement, chemical manufacturing, mineral processing, and more. The ball mill is essential in several applications due to its simple construction, versatility, and ability to handle different materials.
Ball Mill Principle
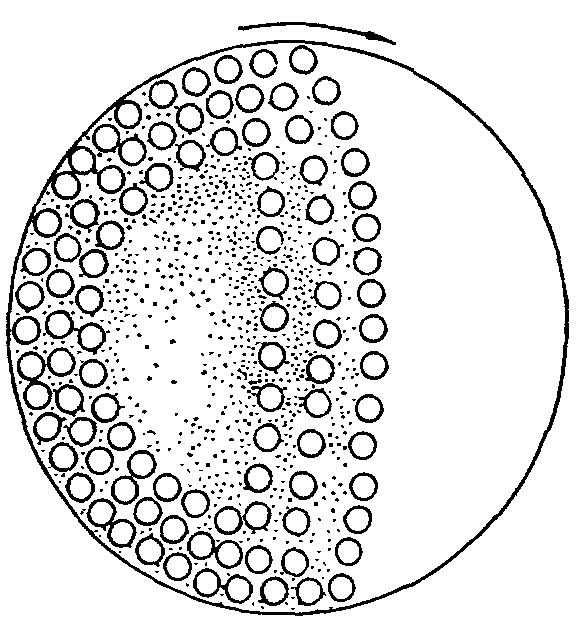
The Ball mill principle revolves around the movement of the grinding media inside a rotating cylindrical drum. As the drum rotates, the balls or other grinding bodies inside the mill rise along the wall of the cylinder, then fall back down due to gravity. This action creates a cascade of balls that impact the material being ground. The continual collision of these balls with the material causes it to break apart, reducing its size. The energy imparted by the falling balls is responsible for the mechanical grinding of the material.
Ball mills can operate in both dry and wet conditions. In the dry method, the material is fed into the mill through a chute or screw, while in wet milling, a system of scoops is used to feed the material into a stationary tank that is then stirred with the rotating mill. The choice between dry or wet milling typically depends on the nature of the material and the desired final product.
The ball mill principle ensures that the grinding process is both efficient and effective. As the shell rotates, the motion of the balls inside creates a cascading effect, which grinds the materials into a desired particle size. This mechanism is widely used in processes such as cement manufacturing, ore beneficiation, and paint production.
Ball mills are designed to handle various materials, from soft powders to hard minerals. Their adaptability and efficiency make them a go-to choice in numerous industrial processes. By leveraging the ball mill principle, industries can achieve consistent results and high-quality outputs.
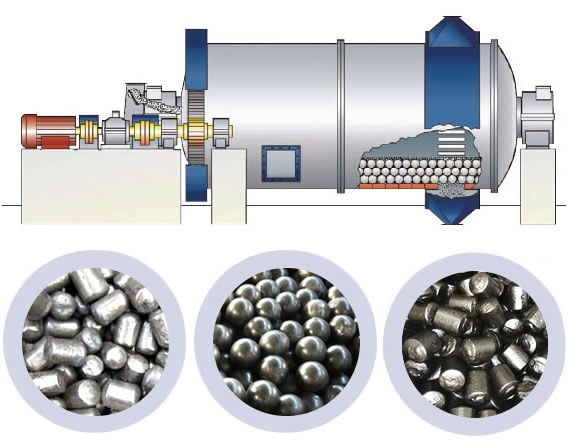
Components of a Ball Mill
A typical ball mill setup includes several key components:
- The Drum: This is the cylindrical or cylindrical-conical container that holds both the material to be ground and the grinding media.
- The Grinding Media: The media can be made of various materials, including steel, cast iron, porcelain, or flint. Steel balls are the most common form of grinding media used in ball mills due to their durability and ability to grind hard materials.
- The Motor: The motor is responsible for rotating the drum, providing the necessary motion to allow the grinding media to move and collide with the material inside.
- The Discharge System: The mill features a discharge system that allows the ground material to exit the drum after grinding. This system can be a trunnion, grate, or overflow, depending on the design of the ball mill.
Working of a Ball Mill
Ball mills can be used for both wet and dry grinding, with the choice depending on the material being processed and the desired final product. In dry grinding, the material is ground without the addition of water, and the ground material is typically finer. This method is commonly used for grinding dry materials such as ores, minerals, and chemicals.
In wet grinding, the material is ground in the presence of water or other liquids. This method is preferred when the material requires a slurry or liquid to enhance the grinding process or to prevent the material from becoming too sticky. Wet grinding is widely used in industries like cement production, mining, and the production of paints and coatings.
Factors Affecting Ball Mill Efficiency
Several factors influence the efficiency and performance of a ball mill. These factors include:
- Size and Shape of Grinding Media: The size of the grinding media affects the grinding efficiency. Larger balls provide more impact force, while smaller balls are more effective in grinding finer materials. The shape of the media also affects the grinding process, with spherical balls being more efficient than irregularly shaped media.
- Mill Speed: The speed of the mill is crucial in determining the energy input and grinding efficiency. Most ball mills operate at speeds between 70–80% of their critical speed, which is the speed at which the grinding media would be held against the wall due to centrifugal force.
- Filling Ratio: The filling ratio of the mill, which refers to the proportion of the mill’s volume occupied by the grinding media, is another important factor. A filling ratio of 30–45% is typically used in ball mills, with about 40% of this being void space.
- Material Hardness: The hardness of the material being ground also plays a significant role. Harder materials require more energy to grind, and the choice of grinding media may need to be adjusted based on the hardness of the material.
- Feed Size: The size of the material fed into the mill also impacts the grinding process. Larger feed sizes require more energy to break down, so materials are often pre-crushed before being fed into the ball mill.
Applications of Ball Mills
Ball mills are widely used in various industries, such as:
- Mining and Mineral Processing: Ball mills are commonly used to grind ores and minerals in the mining industry. They help in the extraction of valuable metals and minerals by breaking down the ore into smaller particles.
- Cement Manufacturing: In cement production, ball mills are used to grind raw materials like limestone and clay into fine powder, which is then used to produce cement.
- Pharmaceuticals and Chemicals: Ball mills are used in the pharmaceutical and chemical industries to produce fine powders for drugs, pigments, and chemicals.
- Food Industry: In the food industry, ball mills are used to grind grains, spices, and other food products.
Conclusion
The Ball mill principle of operation, based on impact and attrition, makes it a versatile and efficient tool for grinding a wide range of materials. By adjusting various parameters such as the size and speed of the mill, the type of grinding media, and the filling ratio, ball mills can be optimized for specific applications. The ball mill’s role in industries such as mining, cement, pharmaceuticals, and food production underscores its importance in manufacturing processes. Understanding the ball mill principle and its efficiency factors is crucial for improving the performance and reducing operational costs in grinding processes.
For more information on grinding media and optimization of ball mills, companies like alphagrindingmedia provide valuable resources and products to enhance the efficiency and longevity of ball mills in industrial applications.
f&q
1. What is the primary purpose of a ball mill?
Ball mills are primarily used for grinding and pulverizing materials into fine powders. They are widely employed in industries like mining, ceramics, and cement manufacturing for producing finely ground materials.
2. Can ball mills be used for both dry and wet grinding?
Yes, ball mills are designed for both dry and wet grinding processes. The choice depends on the material being processed and the desired end result. Wet grinding is often preferred for materials that require finer particle sizes.
3. How do I choose the right grinding media for a ball mill?
Selecting the appropriate grinding media depends on factors like material type, desired particle size, and the grinding process (dry or wet). For professional recommendations, consulting a supplier like Alpha Grinding Media is advisable.
4. What are the common maintenance tasks for ball mills?
Key maintenance tasks include:Regularly inspecting and replacing worn liners.
Checking the condition of grinding media.
Ensuring proper lubrication of moving parts.
Monitoring drum rotation speed to prevent inefficiencies.
By following a consistent maintenance schedule, you can enhance the performance and lifespan of your ball mill.





