Introduction to Sodium Metabisulfite: What It Is and Why It's Used
Sodium metabisulfite (Na2S2O5) is a chemical compound commonly used in various industries for its antioxidant, preservative, and disinfectant properties. It appears as a white or yellowish granulated powder and releases sulfur dioxide (SO2) when dissolved in water.
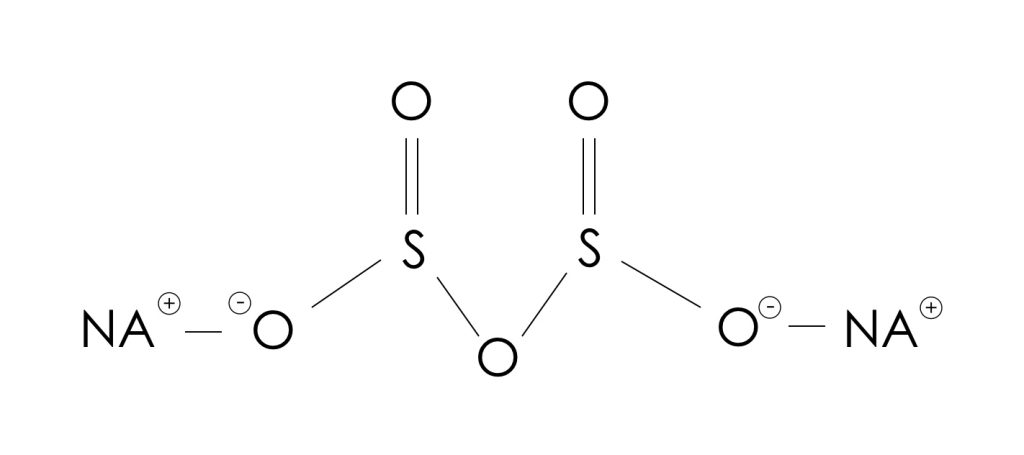
Structure and Properties: Sodium metabisulfite is composed of two sodium ions and one metabisulfite ion.
It is known for its ability to release sulfur dioxide gas, which acts as a powerful reducing agent and antimicrobial agent. This makes sodium metabisulfite useful in preventing oxidation and microbial growth.
Sodium metabisulfite is a versatile chemical compound used in various industrial applications, including mining. In copper and gold mining, it serves as a flotation agent. Specifically, in the context of copper mines, sodium metabisulfite is added to the ball mill—a critical piece of equipment used to crush and grind ore. Its primary role is to enhance the flotation process by selectively modifying the surface properties of minerals, which improves the separation of valuable metals from the ore. By adjusting the flotation conditions, sodium metabisulfite helps in efficiently extracting copper and other precious metals, contributing to the overall effectiveness and productivity of the mining operation.
Common Applications of Sodium Metabisulfite in Various Industries
- Antioxidant in Pharmaceuticals: In pharmaceutical formulations, sodium metabisulfite acts as an antioxidant to prevent the oxidation of active ingredients, thereby maintaining the stability and efficacy of the product.
- Disinfectant: Its disinfectant properties make it valuable in sanitizing equipment and surfaces, particularly in the food and beverage industry.
- Food Preservative: Sodium metabisulfite is used as a preservative in various food products. It helps in inhibiting the growth of unwanted microorganisms and extending the shelf life of foods.
- Juice and Wine Production: In juice and wine production, sodium metabisulfite is often added to fresh juices and musts to kill wild molds and bacteria before fermentation. This ensures a cleaner fermentation process and better quality of the final product.
How It Is Used: In practice, sodium metabisulfite is typically added in small amounts to liquids, such as fresh juices, usually 24 hours before the addition of yeast. This application is crucial for destroying any wild molds or bacteria present in the liquid, preventing spoilage and ensuring successful fermentation.
Overall, sodium metabisulfite is a versatile chemical with significant applications in preserving, disinfecting, and stabilizing various products across multiple industries.
How to Properly Use Sodium Metabisulfite: Dosage and Methods
- Dosage and Application:
Sodium metabisulfite is frequently used in baking as a dough-softening agent. Its typical concentration in flour is about 200 mg per kg. To use it effectively, follow these steps:- Blending with Flour:
Ensure that sodium metabisulfite is thoroughly mixed with the flour. This guarantees even distribution throughout the dough and ensures uniform performance. - Monitor Residual Bisulfite:
Regularly check the residual bisulfite concentration during the process to confirm its effectiveness. This is particularly important if sodium metabisulfite is used alongside other substances, such as chlorine, which can neutralize it. - Check Specific Recipes:
Always refer to specific recipes or guidelines for precise dosages and instructions, as the optimal amount can vary depending on the application and other ingredients used.
- Blending with Flour:
- Safety Precautions:
- Wear Appropriate Personal Protective Equipment (PPE):
- Gloves: Use protective gloves, such as nitrile or latex, to prevent skin contact.
- Eye Protection: Wear safety goggles or a face shield to protect your eyes from potential splashes.
- Respiratory Protection: If working in an area with airborne particles, use a dust mask or respirator.
- Work in a Well-Ventilated Area:
Sodium metabisulfite can release sulfur dioxide gas, which may irritate the respiratory system. Ensure that the area is well-ventilated to avoid inhaling fumes.
Avoid using it in enclosed spaces without adequate ventilation. - Avoid Skin and Eye Contact:
Sodium metabisulfite can irritate skin and eyes. Minimize direct contact, and if it does come into contact, immediately flush the affected area with plenty of water. - Avoid Inhalation:
Do not inhale the powder or dust. Work in a way that reduces the risk of airborne particles.
If inhalation occurs, move to fresh air and seek medical attention if necessary. - Follow Proper Disposal Methods:
Dispose of sodium metabisulfite waste in accordance with local, state, and federal regulations. Do not pour it down drains or dispose of it in regular trash. - Store Properly:
Keep sodium metabisulfite in a tightly sealed container. Store it in a cool, dry, and well-ventilated area.
Avoid storing it near strong acids, as they can release toxic sulfur dioxide gas. - Review Safety Data Sheets (SDS):
Always consult the Safety Data Sheets for detailed information on hazards, handling, and storage.
By following these guidelines, you can ensure the safe and effective use of sodium metabisulfite in your applications.
Storage Guidelines for Sodium Metabisulfite: Keeping It Safe and Effective
To ensure the effectiveness and safety of sodium metabisulfite, proper storage is crucial. Store sodium metabisulfite in tightly closed containers to protect it from air and moisture. Keep it in a cool, dry, and well-ventilated area, away from combustible materials like wood, paper, and oils, which could pose a fire risk. The product should be shielded from heat and physical damage to prevent degradation.
The recommended storage period for sodium metabisulfite is up to 6 months from the date of production. To maintain its efficacy, ensure that containers are sealed properly and stored in conditions that prevent moisture and oxidation. Always follow these guidelines to preserve the chemical’s quality and safety throughout its use.
Safety Precautions When Handling Sodium Metabisulfite
- Personal Protective Equipment (PPE): Wear protective gloves, safety goggles, and a dust mask or respirator to avoid skin, eye, and respiratory exposure.
- Ventilation: Work in a well-ventilated area to prevent inhalation of sulfur dioxide gas released by the compound.
- Avoid Contact: Prevent skin and eye contact. Rinse affected areas with water if contact occurs.
- Minimize Inhalation: Do not inhale dust; work to reduce airborne particles.
- Proper Disposal: Dispose of sodium metabisulfite according to local regulations, avoiding drains and general trash.
- Storage: Store in a cool, dry place, away from combustible materials and strong acids. Ensure containers are tightly sealed.
Benefits of Using Sodium Metabisulfite in Your Processes
Sodium metabisulfite offers several key advantages in various industrial and commercial applications:
- Effective Antioxidant: It helps prevent oxidation in pharmaceutical formulations, thereby maintaining the stability and efficacy of active ingredients.
- Preservative Properties: Used in the food and beverage industry, it acts as a preservative to extend shelf life by inhibiting microbial growth.
- Dough Softening: In baking, it softens dough and improves texture, contributing to better quality baked goods.
- Disinfectant: It serves as a disinfectant in cleaning and sanitizing applications, especially in the food industry, ensuring hygienic conditions.
Frequently Asked Questions About Sodium Metabisulfite
- Sodium metabisulfite is used as an antioxidant, preservative, disinfectant, and dough-softening agent in various industries.
Store sodium metabisulfite in a tightly sealed container in a cool, dry, and well-ventilated area, away from moisture and heat.
Wear protective gloves, safety goggles, and a dust mask. Ensure good ventilation and avoid direct contact with skin and eyes.
Sodium metabisulfite typically remains effective for up to 6 months from the date of production if stored properly.