Ball mill machines are the cornerstone of material processing in industries like mining, cement, ceramics, and chemical manufacturing. These robust machines grind and blend raw materials into fine powders, enabling the production of high-quality products used in everything from construction to advanced technology. This comprehensive guide explores what ball mill machines are, how they work, their applications, benefits, and detailed strategies for optimizing their performance. Whether you’re a mining engineer, cement plant manager, or lab technician, understanding ball mills is key to achieving efficient and cost-effective grinding operations.
What Is a Ball Mill Machine?
A ball mill machine is a cylindrical device designed to pulverize materials into fine particles through mechanical impact and attrition. The machine consists of a rotating drum filled with grinding media—typically steel or ceramic balls—that collide with the material as the drum spins, breaking it down into smaller particles.
Key Components of a Ball Mill
- Rotating Drum: The main chamber where grinding occurs, often lined with durable materials like rubber or steel to withstand wear.
- Grinding Media: Balls made of steel, ceramic, or other materials that crush and grind the material inside the drum.
- Motor and Drive System: Powers the drum’s rotation, typically operating at 20–40 RPM depending on the mill’s size and application.
- Discharge System: Allows the processed material to exit the mill, either as a dry powder or wet slurry.
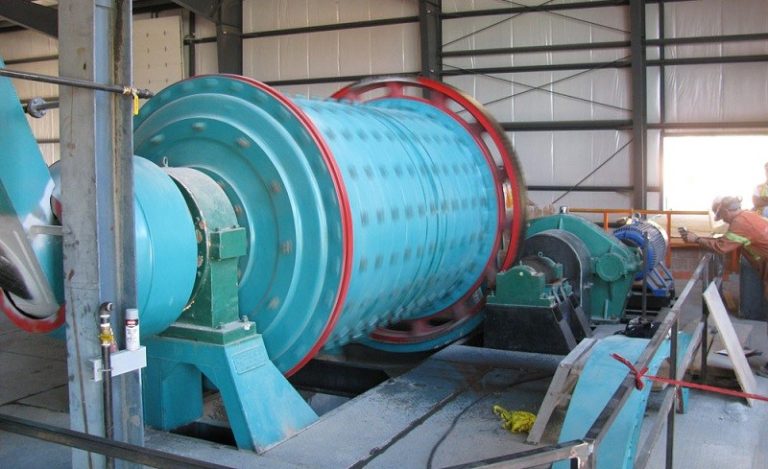

Types of Ball Mills
- Wet Ball Mills: Used for grinding materials in a liquid medium, ideal for slurries in mineral processing or chemical mixing.
- Dry Ball Mills: Designed for grinding dry materials, commonly used in cement production or ceramic powder processing.
- Planetary Ball Mills: Smaller, high-energy mills used in laboratories for ultra-fine grinding and research applications.
Ball mills vary in size, from small lab-scale units (1–5 liters) to large industrial mills (up to 100 tons/hour capacity), making them adaptable to a wide range of industries.
How Ball Mill Machines Work
The working principle of a ball mill is straightforward but highly effective. The drum rotates, causing the grinding media to rise and fall, creating a cascading motion. This motion generates impact and attrition forces that break down the material into finer particles.
- Cascading Motion: At optimal speeds (65–80% of critical speed), the media tumbles, striking the material and grinding it through impact.
- Attrition: As media particles rub against each other and the material, they create friction, further reducing particle size.
- Critical Speed: The speed at which media would stick to the drum’s inner wall (centrifugal force). Operating below this speed ensures effective grinding.
For example, in a typical mining application, a ball mill might rotate at 25 RPM, using 50 mm steel balls to grind gold ore into particles smaller than 100 micrometers for further processing.
Applications of Ball Mill Machines
Ball mill mills are versatile and widely used across industries for grinding and mixing materials. Below are some of the primary applications:
1. Mining Industry
- Ore Processing: Ball mills grind ores like gold, copper, and iron into fine particles for processes like flotation, leaching, or smelting.
- Example: In gold mining, ball mills reduce ore to 75–150 micrometers, improving gold recovery rates in downstream processes.
2. Cement Production
- Clinker Grinding: Ball mills pulverize cement clinker into fine powder, ensuring consistent quality for construction-grade cement.
- Example: A cement plant might use a 50-ton/hour ball mill to produce cement with a fineness of 3,000–4,000 cm²/g (Blaine).
3. Ceramics and Glass
- Powder Production: Ball mills create fine powders for ceramic tiles, pottery, or advanced materials like zirconia and alumina.
- Example: Ceramic manufacturers use ball mills to achieve particle sizes below 50 micrometers for high-quality glazes.
4. Chemical and Pharmaceutical Industries
- Mixing and Grinding: Ball mills produce uniform powders for pigments, fertilizers, or pharmaceutical compounds.
- Example: In paint production, ball mills ensure pigments are finely ground for smooth, consistent coatings.
5. Laboratory Research
- Material Testing: Small-scale planetary ball mills are used in labs to develop new materials or analyze grinding properties.
- Example: Researchers might use a 1-liter planetary mill to grind nanoparticles for advanced composites.
These diverse applications highlight the adaptability of ball mills in achieving precise and efficient material processing.
Benefits of Ball Mill Machines
Ball mills are a preferred choice for grinding due to their unique advantages:
- High Grinding Efficiency: Capable of reducing materials to very fine sizes (down to 10–100 micrometers), ensuring high-quality output.
- Versatility: Suitable for both wet and dry grinding, accommodating materials like ores, chemicals, and ceramics.
- Scalability: Available in a range of sizes, from small lab mills to large industrial units, meeting diverse production needs.
- Durability: Robust designs with wear-resistant liners (e.g., rubber or manganese steel) ensure long-term reliability.
- Cost-Effectiveness: Low maintenance costs and reusable grinding media make ball mills economical for continuous operation.
These benefits make ball mills indispensable for industries requiring consistent and efficient material processing.
Optimizing Ball Mill Performance
To maximize the efficiency and lifespan of your ball mill, consider these detailed strategies:
1. Select the Right Grinding Media
The choice of grinding media significantly impacts mill performance:
- Material: Steel balls are ideal for hard materials like ores, while ceramic balls suit softer materials like chemicals or ceramics.
- Size: Smaller balls (10–20 mm) are best for fine grinding, while larger balls (50–100 mm) excel in coarse grinding.
- Example: For copper ore, 40–60 mm forged steel balls provide optimal impact and grinding efficiency.
2. Control Rotation Speed
- Optimal Range: Operate the mill at 65–80% of its critical speed (calculated as Nc = 42.3/√D, where D is the drum diameter in meters).
- Impact: Too high a speed causes media to stick to the drum, reducing grinding efficiency; too low reduces impact force.
- Example: A 3-meter diameter mill should rotate at 20–25 RPM for efficient grinding.
3. Manage Material Feed Rate
- Consistency: Maintain a steady feed rate to avoid overloading (which reduces efficiency) or underloading (which wastes energy).
- Example: For cement clinker, a feed rate of 15–25 tons/hour ensures optimal throughput in a large industrial mill.
4. Monitor Grinding Media Charge
- Volume: Fill the mill to 40–50% of its volume with grinding media for optimal tumbling action.
- Replenishment: Regularly check media wear and add new balls to maintain consistent grinding performance.
- Example: In mining, replenish 10–15% of media monthly to compensate for wear.
5. Perform Regular Maintenance
- Liner Inspection: Replace worn liners (e.g., rubber or steel) every 6–12 months, depending on material abrasiveness.
- Media Quality: Use high-quality media, like Alpha’s forged steel balls, to minimize wear and maximize grinding efficiency.
- Lubrication: Lubricate bearings and gears weekly to prevent mechanical failures and ensure smooth operation.
By implementing these strategies, you can achieve higher throughput, better particle size control, and lower operational costs.
Choosing the Right Ball Mill for Your Industry
Selecting the right ball mill depends on your specific needs:
- Wet vs. Dry Grinding: Choose wet mills for slurries (e.g., mineral processing) and dry mills for powders (e.g., cement production).
- Capacity: Small mills (1–5 tons/hour) are suitable for labs or small plants, while large mills (50–100 tons/hour) serve industrial applications.
- Lining Material: Rubber linings reduce wear for abrasive materials, while steel linings are better for heavy-duty grinding.
- Grinding Media: Match media to the material (e.g., steel balls for ores, ceramic for chemicals) to optimize performance.
Alpha Grinding Media offers a range of high-quality grinding media, such as forged and high-chrome steel balls, to ensure your ball mill operates at peak efficiency.
Challenges and Solutions in Ball Mill Operations
While ball mills are highly effective, they can face challenges. Here are common issues and how to address them:
- Overheating: Caused by high rotation speeds or excessive media charge. Solution: Reduce speed to 65–75% of critical and optimize media volume.
- Uneven Particle Size: Due to improper media size or feed rate.
Solution: Use a mix of media sizes (e.g., 30–60 mm) and maintain a consistent feed. - Liner Wear: Abrasive materials can damage
liners. Solution: Use durable linings (e.g., manganese steel) and inspect regularly. - Low Efficiency: Caused by worn media or suboptimal settings. Solution: Replace media regularly and fine-tune speed and feed parameters.
Addressing these challenges proactively ensures consistent performance and minimizes downtime.
Conclusion
Ball mill machines are critical for efficient material processing in industries like mining, cement, ceramics, and chemicals. Their ability to grind materials into fine powders with high precision and versatility makes them indispensable for producing high-quality products. By selecting the right grinding media, optimizing rotation speed, managing feed rates, and performing regular maintenance, you can maximize the efficiency and longevity of your ball mill. Understanding the applications, benefits, and optimization techniques of ball mills empowers you to achieve better results, reduce costs, and stay competitive in your industry. With the right approach, ball mill machines can transform your material processing operations.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. What materials can be processed in a ball mill machine?
Ball mills can process a wide range of materials, including ores (e.g., gold, copper, iron), cement clinker, ceramics, chemicals, and pigments. The choice of grinding media (steel or ceramic) depends on the material’s hardness and desired particle size.
2. What’s the difference between wet and dry ball mills?
Wet ball mills grind materials in a liquid slurry, ideal for mineral processing or chemical mixing, while dry ball mills process powders, suitable for cement or ceramic production. Wet mills often achieve finer particles but require additional drying steps.
3. How do I choose the right grinding media for my ball mill?
Select media based on material hardness and grinding goals. Steel balls are ideal for hard materials like ores, while ceramic balls suit softer materials like chemicals. Smaller media (10–20 mm) are best for fine grinding, while larger media (50–100 mm) excel in coarse grinding.
4. How can I improve the energy efficiency of my ball mill?
To boost energy efficiency, operate at 65–80% of critical speed, use a balanced media charge (40–50% of drum volume), maintain consistent feed rates, and choose high-quality grinding media to reduce wear and energy loss.





