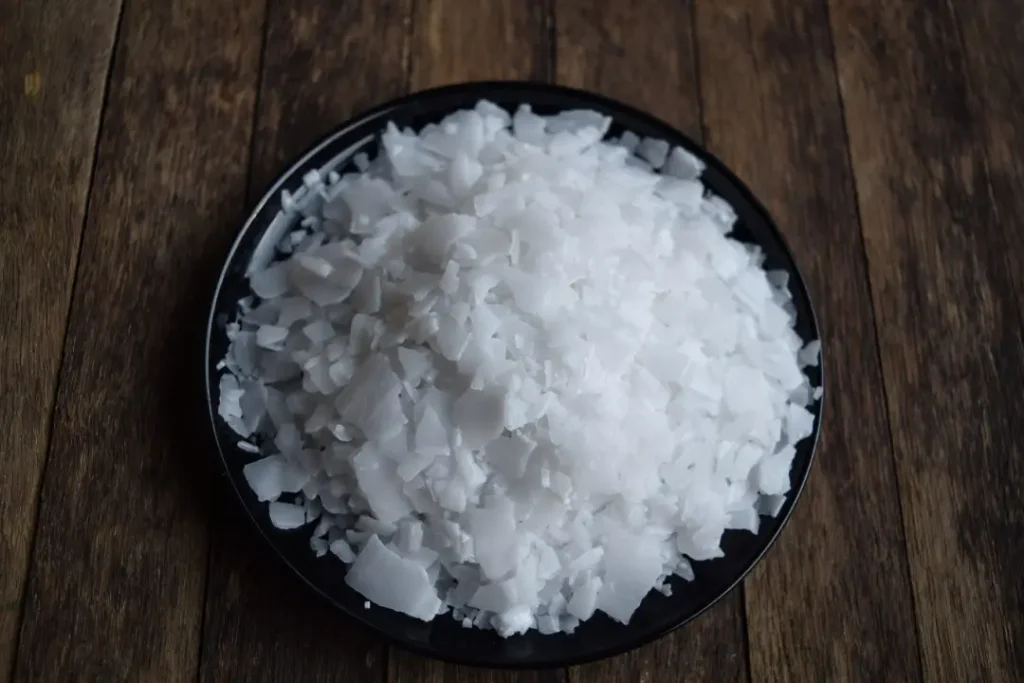
Caustic soda, also known as sodium hydroxide (NaOH), is a powerful and versatile alkaline compound with a wide range of industrial applications. As one of the most commonly used chemicals worldwide, it plays an important role in various sectors including manufacturing, water treatment, and chemical production. In this article from Alpha Grinding Media, we will explore the properties of caustic soda and examine its physical, chemical, and functional characteristics that make it essential in various industries.
Physical Properties of Caustic Soda
Caustic soda exists primarily as a white, odorless solid in its pure form, which is highly hygroscopic, meaning it readily absorbs water from the air. It is most commonly available in the form of pellets, flakes, or a concentrated liquid solution. When dissolved in water, caustic soda forms a highly exothermic solution, releasing a significant amount of heat. This reaction highlights one of its key characteristics: its highly reactive nature.
The solubility of caustic soda in water is extremely high, making it an effective solvent for various applications. At room temperature, approximately 111 grams of sodium hydroxide can dissolve in 100 milliliters of water. When dissolved, the solution becomes strongly basic, with a pH that can reach up to 14 in concentrated forms. This extreme alkalinity is what gives caustic soda its powerful corrosive properties.
Chemical Properties of Caustic Soda
The chemical properties of caustic soda are what make it useful in many industrial processes. Sodium hydroxide is a strong base, and it readily dissociates in water to produce hydroxide ions (OH⁻) and sodium ions (Na⁺). This dissociation leads to its highly alkaline nature and enables it to neutralize acids, making it an essential ingredient in acid-base reactions.
One of the most important chemical properties of caustic soda is its ability to act as a powerful corrosive agent. It can react with a wide variety of substances, including metals, glass, and organic materials. For instance, when caustic soda comes into contact with aluminum, it forms sodium aluminate, releasing hydrogen gas in the process. This reaction exemplifies the corrosive nature of sodium hydroxide.

Caustic soda can also participate in saponification, a reaction with fats or oils to produce soap and glycerin. This chemical property is what makes caustic soda a key ingredient in soap manufacturing. Similarly, in the textile industry, it is used to break down natural fibers during the process of bleaching and dyeing fabrics.
Another important chemical property of caustic soda is its ability to facilitate the process of hydrolysis, which is the breakdown of compounds when water is added. This property makes caustic soda a critical component in various chemical syntheses, including the production of biodiesel, where it helps in the transesterification of fats into fatty acid methyl esters (biodiesel) and glycerol.
Industrial Applications of Caustic Soda
Given its highly reactive and corrosive properties, caustic soda has a broad spectrum of industrial applications. It is a key player in several industries, including chemical manufacturing, petroleum refining, paper production, water treatment, and food processing.
- Chemical Manufacturing: Caustic soda is used extensively in the production of various chemicals, such as chlorine, plastics (PVC), and synthetic fibers. The process of chlor-alkali production, which involves the electrolysis of sodium chloride (salt), results in the creation of both chlorine and sodium hydroxide. This makes caustic soda a critical component in the chemical industry.
- Petroleum Refining: In petroleum refining, caustic soda is used to remove sulfur and other impurities from crude oil. This process, known as caustic washing or sweetening, helps improve the quality of the final petroleum products, such as gasoline and diesel.
- Paper and Pulp Industry: Caustic soda plays a vital role in the paper and pulp industry, where it is used in the Kraft process to break down wood into cellulose fibers. The solution of sodium hydroxide helps dissolve lignin, the substance that binds the fibers together, enabling the production of high-quality paper.
- Water Treatment: Caustic soda is used in water treatment plants to adjust the pH of water and neutralize acidic compounds. It is also employed in the precipitation of heavy metals and in softening hard water by removing calcium and magnesium ions.
- Food Processing: In food processing, caustic soda is used for tasks such as peeling fruits and vegetables, making soft drinks, and processing certain edible oils. However, its use in food products is carefully regulated, as it can be harmful if not used correctly.
Cleaning and Degreasing: Due to its strong alkaline nature, caustic soda is an effective cleaner and degreaser. It is commonly used in cleaning industrial equipment, including machinery in the food and beverage industry, as well as in residential and commercial drain cleaners.
Safety Considerations and Handling of Caustic Soda
Despite its usefulness, caustic soda poses significant health and safety risks due to its corrosive nature. Direct contact with sodium hydroxide, whether in solid or liquid form, can cause severe burns, permanent tissue damage, and even blindness. Inhaling its fumes can lead to respiratory irritation and damage to the respiratory tract.
When handling caustic soda, proper personal protective equipment (PPE), such as gloves, goggles, and protective clothing, should always be worn. Additionally, caustic soda should be stored in tightly sealed containers to prevent it from reacting with moisture in the air. Adequate ventilation should be maintained in areas where it is used or stored to prevent the buildup of potentially hazardous fumes.
In case of skin contact, the affected area should be flushed immediately with copious amounts of water to minimize the risk of burns. For eye contact, it is crucial to irrigate the eyes with water for at least 15 minutes and seek medical attention as soon as possible. Spills should be neutralized with dilute acid, such as vinegar, before being cleaned up.
Environmental Impact and Disposal
While caustic soda is essential for many industrial processes, its impact on the environment must be considered. Improper disposal of sodium hydroxide can lead to soil and water contamination, harming aquatic life and disrupting ecosystems. Therefore, it is crucial to follow appropriate disposal protocols when handling waste that contains caustic soda.
In many industrial settings, waste caustic soda can be neutralized with acids to form salts, which can be safely disposed of or further processed. Additionally, wastewater treatment plants often have specific procedures to handle the neutralization of sodium hydroxide before discharging water back into the environment.
Conclusion
The properties of caustic soda make it an indispensable chemical in various industries, from manufacturing and petroleum refining to food processing and water treatment. Its highly reactive nature, ability to dissolve a wide range of materials, and powerful alkaline characteristics provide a broad spectrum of applications that contribute significantly to modern industrial processes.
However, it is essential to recognize the potential hazards associated with handling and disposing of caustic soda. Proper safety measures, storage protocols, and disposal practices must be followed to mitigate the risks posed by this powerful compound. By understanding and respecting the properties of caustic soda, industries can continue to harness its benefits while ensuring the safety of workers and the environment.
For more information on the industrial uses of caustic soda, including its role in grinding media applications, visit Alpha Grinding Media’s website. Their resources provide detailed insights into how caustic soda is utilized in various industrial processes.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. What are the physical characteristics of caustic soda?
Caustic soda is a white, odorless solid that is highly hygroscopic, meaning it absorbs moisture from the air. It is typically available in the form of pellets, flakes, or as a concentrated liquid.
2. How does caustic soda react when mixed with water?
When caustic soda is dissolved in water, it forms an exothermic reaction, releasing a significant amount of heat. The resulting solution is highly alkaline, with a pH that can reach up to 14 in concentrated forms.
3. What are the main industrial uses of caustic soda?
Caustic soda is widely used in industries such as chemical manufacturing, petroleum refining, paper production, water treatment, and food processing, among others. It plays a key role in neutralizing acids, breaking down fats in soap-making, and removing impurities in various chemical processes.
4. How should caustic soda be safely handled?
Given its corrosive properties, caustic soda should be handled with caution. It is essential to wear appropriate protective equipment like gloves, goggles, and protective clothing. In case of skin contact, it should be washed immediately with water, and in case of eye contact, immediate irrigation with water for at least 15 minutes is necessary.





